Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor
The three phase induction motor is the most widely used electrical motor. Almost 80% of the mechanical power used by industries is provided by three phase induction motors because of its simple and rugged construction, low cost, good operating characteristics, the absence of commutator and good speed regulation. In three phase induction motor, the power is transferred from stator to rotor winding through induction. The induction motor is also called a synchronous motor as it runs at a speed other than the synchronous speed.
Like any other electrical motor induction motor also have two main parts namely rotor and stator.
1. Stator: As its name indicates stator is a stationary part of induction motor. A stator winding is placed in the stator of induction motor and the three phase supply is given to it.
2. Rotor: The rotor is a rotating part of induction motor. The rotor is connected to the mechanical load through the shaft.
1. Squirrel cage rotor,
2. Slip ring rotor or wound rotor or phase wound rotor.
Depending upon the type of rotor construction used the three phase induction motor are classified as:
1. Squirrel cage induction motor,
2. Slip ring induction motor or wound induction motor or phase wound induction motor.
Stator of Three Phase Induction Motor:
The stator of the three-phase induction motor consists of three main parts :
1. Stator frame,
2. Stator core,
3. Stator winding or field winding.
Stator Frame:
It is the outer part of the three phase induction motor. Its main function is to support the stator core and the field winding. It acts as a covering, and it provides protection and mechanical strength to all the inner parts of the induction motor. The frame is either made up of die-cast or fabricated steel. The frame of three phase induction motor should be strong and rigid as the air gap length of three phase induction motor is very small. Otherwise, the rotor will not remain concentric with the stator, which will give rise to an unbalanced magnetic pull.
Stator Core:
The main function of the stator core is to carry the alternating flux. In order to reduce the eddy current loss, the stator core is laminated. These laminated types of structure are made up of stamping which is about 0.4 to 0.5 mm thick. All the stamping are stamped together to form stator core, which is then housed in stator frame. The stamping is made up of silicon steel, which helps to reduce the hysteresis loss occurring in the motor.
Stator Winding or Field Winding:
The slots on the periphery of the stator core of the three-phase induction motor carry three phase windings. We apply three phase ac supply to this three-phase winding. The three phases of the winding are connected either in star or delta depending upon which type of starting method we use. We start the squirrel cage motor mostly with star-delta stator and hence the stator of squirrel cage motor is delta connected. We start the slip ring three-phase induction motor by inserting resistances so, the stator winding of slip ring induction motor can be connected either in star or delta. The winding wound on the stator of three phase induction motor is also called field winding, and when this winding is excited by three phase ac supply, it produces a rotating magnetic field
Types of Three Phase Induction Motor:
1. Squirrel Cage Three Phase Induction Motor:
The rotor of the squirrel cage three phase induction motor is cylindrical and have slots on its periphery. The slots are not made parallel to each other but are bit skewed (skewing is not shown in the figure of squirrel cage rotor besides) as the skewing prevents magnetic locking of stator and rotor teeth and makes the working of the motor more smooth and quieter. The squirrel cage rotor consists of aluminum, brass or copper bars (copper bras rotor is shown in the figure beside). These aluminum, brass or copper bars are called rotor conductors and are placed in the slots on the periphery of the rotor. The rotor conductors are permanently shorted by the copper, or aluminum rings called the end rings. To provide mechanical strength, these rotor conductors are braced to the end ring and hence form a complete closed circuit resembling like a cage and hence got its name as squirrel cage induction motor. The squirrel cage rotor winding is made symmetrical. As end rings permanently short the bars, the rotor resistance is quite small, and it is not possible to add external resistance as the bars get permanently shorted. The absence of slip ring and brushes make the construction of Squirrel cage three-phase induction motor very simple and robust and hence widely used three phase induction motor. These motors have the advantage of adopting any number of pole pairs. The below diagram shows a squirrel cage induction rotor having aluminum bars short circuit by aluminum end rings.
Advantages of Squirrel Cage Induction Rotor:
1. Its construction is very simple and rugged.
2. As there are no brushes and slip ring, these motors requires less maintenance.
Applications of Squirrel Cage Induction Rotor:
We use the squirrel cage induction motors in lathes, drilling machine, fan, blower printing machines, etc
2. Slip Ring or Wound Rotor Three Phase Induction Motor:
In this type of three phase induction motor the rotor is wound for the same number of poles as that of the stator, but it has less number of slots and has fewer turns per phase of a heavier conductor. The rotor also carries star or delta winding similar to that of the stator winding. The rotor consists of numbers of slots and rotor winding are placed inside these slots. The three end terminals are connected together to form a star connection. As its name indicates, three phase slip ring induction motor consists of slip rings connected on the same shaft as that of the rotor. The three ends of three-phase windings are permanently connected to these slip rings. The external resistance can be easily connected through the brushes and slip rings and hence used for speed controlling and improving the starting torque of three phase induction motor. The brushes are used to carry current to and from the rotor winding. These brushes are further connected to three phase star connected resistances. At starting, the resistance is connected to the rotor circuit and is gradually cut out as the rotor pick up its speed. When the motor is running the slip ring are shorted by connecting a metal collar, which connects all slip ring together, and the brushes are also removed. This reduces the wear and tear of the brushes. Due to the presence of slip rings and brushes the rotor construction becomes somewhat complicated therefore it is less used as compare to squirrel cage induction motor.
Advantages of Slip Ring Induction Motor:
1. It has high starting torque and low starting current.
2. Possibility of adding additional resistance to control speed.
Application of Slip Ring Induction Motor:
Slip ring induction motor are used where high starting torque is required i.e in hoists, cranes, elevator etc
Difference between Slip Ring and Squirrel Cage Induction Motor:
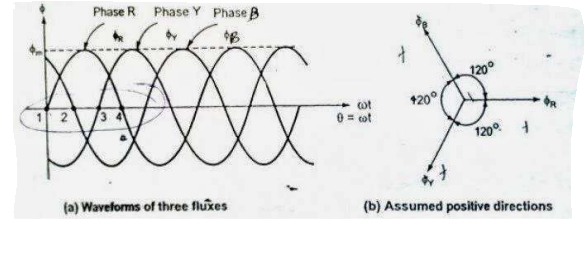
Production of Rotating Magnetic Field: The production of Rotating magnetic field in 3 phase supply is very interesting. When a 3-phase winding is energized from a 3-phase supply, a rotating magnetic field is produced. This field is such that its poles do no remain in a fixed position on the stator but go on shifting their positions around the stator. For this reason, it is called a rotating field. It can be shown that magnitude of this rotating field is constant and is equal to 1.5 fm where fm is the maximum flux due to any phase.
A three phase induction motor consists of three phase winding as its stationary part called stator. The three phase stator winding is connected in star or delta. The three phase windings are displaced from each other by 120°. The windings are supplied by a balanced three phase ac supply
The three phase currents flow simultaneously through the windings and are displaced from each other by 120° electrical. Each alternating .phase current produces its own flux which is sinusoidal. So all three fluxes are sinusoidal and are separated from each other by 120°. If the phase sequence of the windings is R-Y-B, then mathematical equations for the instantaneous values of the three fluxes ΦR , ΦY , ΦB can be written as,
ΦR = Φmsin(ωt)
ΦY = Φmsin(ωt - 120)
ΦB = Φmsin(ωt - 240)
As windings are identical and supply is balanced, the magnitude of each flux is Φm .
ωt = 0
ΦR = Φmsin(0) = 0
ΦY = Φmsin(0 - 120) = -0.866 Φm
ΦB = Φmsin(0 - 240) = +0.866 Φm
Case 2 :
ωt = 60
ΦR = Φmsin(60) = +0.866 Φm
ΦY = Φmsin(- 60) = -0.866 Φm
ΦB = Φmsin(- 180) = 0
Case 3 :
ωt = 120
ΦR = Φmsin(120) = +0.866 Φm
ΦY = Φmsin(0) = 0
ΦB = Φmsin(- 120) = -0.866 Φm
Case 4 :
ωt = 180
ΦR = Φmsin(180) = 0
ΦY = Φmsin(60) = +.866 Φm
ΦB = Φmsin(- 60) = -0.866 Φm
By comparing the electrical and phasor diagrams we can find the the flux rotates one complete 360 degree on the 180 degree displacement of flux.
Effect of Frequency on Rotor Parameter in the Three Phase Induction Motor:Rotor emf
When the three phase supply is given to the three phase induction motor, the rotating magnetic field is produced which rotates at synchronous speed.
Starting condition:
- The speed of the rotor during starting condition is zero therefore the relative speed between stator rotating magnetic field and rotor speed is Ns – N = Ns
- When the rotor conductors cut the rotating magnetic field, an emf will be induced in it.
- Let us consider that the induced emf in the rotor is E2
Running condition:
- Let us assume that the induced emf in the rotor is E2’. The relative speed between stator rotating magnetic field and rotor speed is Ns – N.
- The induced emf in the rotor condition is
Relative speed Rotor emf
Ns E2
Ns – N E2’
E2’ = [ Ns – N / Ns ] E2
E2’ = s E2
- The slip at starting is unity therefore the rotor induced emf is same as that of starting condition.
- However the rotor induced emf decreases as the speed increases or slip decreases.